How Indian Universities are Incorporating Universal Design for Learning (UDL)
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) is an innovative educational framework that aims to cater to the diverse learning needs of students. UDL is based on the principle that all learners have unique needs and abilities, and educational systems should be flexible enough to accommodate those differences. In the context of higher education, UDL helps ensure that every student, regardless of their abilities or disabilities, has an equal opportunity to learn and succeed.
In India, the integration of UDL principles in universities is slowly gaining momentum as institutions recognize the importance of creating inclusive educational environments. By implementing UDL, universities aim to provide multiple pathways for learning, offering flexible approaches to teaching that accommodate the diverse needs of students. In this blog, we will explore how Indian universities are incorporating UDL and the benefits this approach brings to students with diverse learning requirements.
1. What is Universal Design for Learning (UDL)?
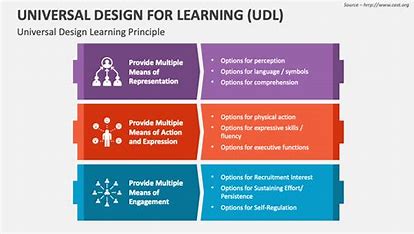
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) is a framework for creating an inclusive classroom environment. UDL’s main focus is on providing multiple means of representation, engagement, and expression to ensure all students have access to learning in a way that works best for them. It is built around three key principles:
- Multiple Means of Representation: Presenting information in different ways (e.g., text, visuals, audio, video) to accommodate various learning styles.
- Multiple Means of Engagement: Providing various ways to engage students, including interactive discussions, group work, hands-on activities, and digital media to maintain interest and motivation.
- Multiple Means of Expression: Allowing students to demonstrate what they have learned in different ways, such as through written essays, oral presentations, videos, or projects.
By applying UDL, educational institutions aim to eliminate barriers to learning, providing all students with equal opportunities for success.
2. Incorporating UDL in Indian Universities
Although UDL is still relatively new in many Indian universities, several leading institutions have already taken significant steps to incorporate UDL principles into their teaching practices. The following are some ways in which Indian universities are adopting UDL:
a) Flexible Learning Materials and Resources
Many Indian universities are starting to create and offer multimedia learning materials that cater to different learning preferences. By offering learning resources in varied formats (text, audio, video, etc.), these institutions are addressing the diverse needs of students.
- Digital Content and Online Resources: Universities are increasingly providing e-learning platforms with accessible content. For example, video lectures with subtitles, audio materials, and interactive e-books help students who have different preferences for consuming information. For students with disabilities, these resources are often designed to be compatible with assistive technologies such as screen readers.
- Accessible Course Materials: Textbooks, lecture notes, and study materials are being made available in accessible formats, including Braille or large print for visually impaired students, and digital formats compatible with assistive devices.
Institutions like the Indian Institute of Technology (IITs) and Delhi University (DU) are making strides by offering digital textbooks and e-learning tools that ensure information is available in diverse formats for better accessibility.
READ MORE
b) Use of Assistive Technology
Another key aspect of UDL is the use of assistive technology to support students in accessing and engaging with the learning material. Many universities in India have integrated assistive technologies to enhance the learning experience for students with disabilities.
- Screen Readers and Speech Recognition: Universities are incorporating screen reader software and speech-to-text technologies to assist students with visual impairments or learning disabilities. Students with reading disabilities, such as dyslexia, can benefit from these tools that convert text to speech or provide auditory support.
- Interactive Tools: Tools like interactive whiteboards, touch-screen devices, and digital pens are becoming common in classrooms, helping students engage with the material in multiple ways.
For instance, IIT Delhi has developed initiatives to integrate assistive technology into classrooms, allowing students with disabilities to participate actively in learning without limitations.
c) Flexible Assessment Methods
Incorporating flexible assessment strategies is a key element of UDL, as it gives students different options to demonstrate their knowledge and abilities. This approach is particularly beneficial for students with disabilities who may face challenges with traditional testing methods.
- Variety of Assessment Formats: Indian universities are introducing alternative assessments such as project-based evaluations, oral exams, presentations, and group discussions to give students more ways to express their knowledge.
- Extended Time for Exams: Many institutions are allowing extra time for students with disabilities or students who need additional time to complete assignments and exams. This is crucial for learners who may require more time due to physical or cognitive challenges.
Tata Institute of Social Sciences (TISS) is one example where professors use flexible evaluation methods, such as projects and presentations, to accommodate diverse learning needs.
d) Faculty Training and Awareness
Faculty training is critical in ensuring that UDL principles are effectively applied in the classroom. Several universities in India are working to educate and sensitize their teaching staff about the importance of inclusive teaching methods.
- Workshops and Training Programs: Universities like Jamia Millia Islamia (JMI) and University of Delhi (DU) have organized workshops for faculty members on how to implement UDL strategies in the classroom. These workshops often focus on how to modify teaching techniques, use technology effectively, and create inclusive syllabi that support diverse learning needs.
- Sensitization on Disability Awareness: To promote inclusivity, universities are incorporating disability awareness programs as part of faculty development. These programs help faculty understand the challenges faced by students with disabilities and the importance of inclusive teaching.
e) Promoting Collaborative Learning Environments
Collaboration among students is a key element of UDL that fosters peer-to-peer learning, providing an opportunity for all students to learn from one another. Indian universities are increasingly adopting collaborative learning environments to ensure inclusivity and diversity.
- Group Discussions and Peer Learning: Group assignments, class discussions, and collaborative projects give students the chance to interact and learn together, sharing their strengths and learning from each other’s perspectives. This helps create a more inclusive learning environment where students can collaborate regardless of their abilities.
- Inclusive Classroom Settings: In some universities, classroom layouts have been redesigned to accommodate students with different needs. Flexible seating arrangements and the use of technology to facilitate communication (e.g., using apps for collaborative work) ensure that every student can participate.
For example, Shiv Nadar University has adopted collaborative learning environments where students with diverse needs can work together on projects, improving accessibility and peer support.
f) Support Services for Students with Disabilities
Incorporating UDL goes hand-in-hand with the provision of dedicated support services for students with disabilities. Many universities are now setting up Disability Resource Centers (DRCs) or Equal Opportunity Cells (EOCs) that offer tailored support for students with disabilities.
- Counseling and Academic Support: These centers offer counseling services, mentoring, and academic assistance to help students navigate their courses and manage their challenges. They also offer resources for students with disabilities, such as note-takers, sign language interpreters, or assistive technologies.
- Mentorship Programs: Mentorship programs, particularly for students with disabilities, help guide them through their academic journey, ensuring they receive the support they need to succeed.
Banaras Hindu University (BHU) and University of Mumbai have established such support structures, ensuring that students with disabilities receive the necessary accommodations and guidance.
3. Benefits of UDL in Indian Universities
The adoption of UDL in Indian universities has several significant benefits for students, faculty, and the overall academic environment. These benefits include:
- Increased Engagement: By offering multiple ways to access and engage with learning materials, students are more likely to stay engaged in the learning process, resulting in better academic performance.
- Improved Accessibility: UDL ensures that learning materials and teaching methods are accessible to students with disabilities, helping to create a more inclusive and equitable learning environment.
- Fostering Independence: UDL encourages students to take ownership of their learning by providing them with choices and options for how they engage with content and demonstrate their knowledge.
- Enhanced Faculty Development: Faculty members learn valuable skills in inclusive teaching methods, which not only help students with disabilities but also improve the overall quality of education for all students.
Conclusion
The integration of Universal Design for Learning (UDL) in Indian universities is still in its early stages, but it is slowly gaining momentum as institutions recognize the need for inclusivity and diversity in education. By providing flexible learning environments, using assistive technologies, and offering varied assessments, universities are making strides to ensure that all students—regardless of their abilities—can succeed.
Institutions like IIT Delhi, Jamia Millia Islamia, University of Delhi, and others are at the forefront of adopting UDL practices. As more universities in India continue to embrace UDL principles, we can expect to see a more inclusive educational system that caters to the diverse learning needs of all students, paving the way for a brighter, more equitable future for education in India.